Study Tour on Innovative Technologies and Good Practices for Air Pollution Control
Korea, 18th - 21st September 2023
Sudokwon Landfill Site
The Asian and Pacific Centre for Transfer of Technology (APCTT) spearheads the project titled "Enhanced capabilities to adopt innovative technologies for city air pollution control in select countries of the Asia-Pacific" aiming to strengthen policies and action plans for air pollution control in Gurugram, Dhaka, and Bangkok. Supported by the Korea-ESCAP Cooperation Fund (KECF), the project supports ESCAP member States to strengthen policies and city level action plans to facilitate adoption of innovative technologies for air pollution control in Asia-Pacific.
The primary objectives of the project are,
- improved availability of knowledge on air pollution control technologies, innovations and good practices
- better understanding of technology needs and gaps for air pollution control in the selected cities
- increased awareness and capacity of city officials and stakeholders to strengthen action plans for adoption of innovative technologies to control air pollution
About the Study Tour
The Study Tour on Innovative Technologies and Good Practices for Air Pollution Control is part of APCTT's ongoing efforts to enhance the capacity of city officials and stakeholders in select countries of the Asia-Pacific region to foster cleaner, greener cities in the Asia-Pacific region. The visiting team consisted of Government officials working at the policy level on air pollution and related issues, project team leaders of target cities and technology experts from the three countries.
Photo caption: Representatives from Bangladesh, India, Thailand and APCTT Staff at South Korea
Key Objectives of the Study Tour
In line with the project's goals, a multi-national team comprised of 10 representatives from Bangladesh, India, and Thailand, along with three APCTT staff members, embarked on a four-day study tour to South Korea from the 18th to the 21st of September 2023. This study tour had several key objectives:
1. Gaining Insights from Korean Innovations: The primary goal of the study tour was to gain valuable insights into innovative air quality management systems and pollution control measures implemented by Korean authorities and institutions.
2. Policy-Level Engagement: The participants included government officials working at the policy level on air pollution issues, project team leaders from the target cities, and technology experts from the three countries.
Photo caption: Opening session at the ESCAP East and Northeast Asia Sub Regional Office (SRO)
Learning Highlights
- Learning from Korea’s Incheon Metropolitan City Council
During the study tour, participants visited the Incheon Metropolitan City Council and were presented with a comprehensive lecture on Incheon's government policies and regulations concerning air quality management. Key aspects discussed included:
- The air quality management system
- The roles of various stakeholders, including research institutions, citizens, industry, and national and local governments
- Regulations, policies, and incentives for air quality improvement
- Efforts to involve all citizens in anti-pollution initiatives
Photo caption: Visit to Incheon City Hall, and the Incheon Metropolitan City Council
- Learning from Shinincheon Combined Cycle Power Plant of Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO)
The participants had the opportunity to explore the Shinincheon Combined Cycle Power Plant operated by the Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO). This facility is at the forefront of air pollution control research and innovation. It focuses on measures developed by the KEPCO Research Institute (KEPRI) for pollutant removal, like emission-pollutant removal systems for gas turbine using catalysts, production of catalyst modules, experimental plant for reduction of pollutants using temperature-based catalysts, selective catalytic reduction, and Ammonia oxidation catalysts.
- Learning from Seoul Metropolitan City Council
The study tour continued with a visit to the Seoul City Hall, where participants learned about Seoul's ambitious policies to mitigate air pollution. The "Clearer Seoul 2030" initiative, aimed at reducing air pollutants by half by 2030, was a highlight. Strategies discussed included incentives for electric vehicles, restricted operation of polluting vehicles, and real-time monitoring of air pollution trends. Participants also visited the city level real-time automobile management system dashboard powered by artificial intelligence for tracking and predicting air pollution trends and entry of polluting vehicles into Seoul City.
Automobile management system dashboard for tracking air pollution at Seoul Metropolitan City Council
- Learning from Resource recovery facility of Seoul Metropolitan Government in Gangnan
The participants next visited the Resource Recovery Facility of Seoul Metropolitan Government in Gangnan, which included an incinerator plant that transforms waste into energy. The facility's impressive capacity (900 tons per day), automated waste segregation methods, and positive impact on reducing landfill and neighborhood heating were noteworthy.
Resource Recovery Facility of Seoul Metropolitan Government in Gangnan
- Learning from Environmental Satellite Monitoring Centre at National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER)
During the tour, the participants also visited the Environmental Satellite Monitoring Centre at the National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER). Here, they learned about the use of the world's first geostationary satellite GEMS (GK-2B), equipped with the Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS), to monitor air pollutants and climate change-causing pollutants in Korea and neighboring countries in real-time. Opportunities for joint research and development of remote sensing instruments were discussed. The Centre offered to share data with visiting countries on demand.
The Environmental Satellite Monitoring Centre at the National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER)
- Learning from Transportation Pollution Research Center at NIER
Another important visit was to the Transportation Pollution Research Center at NIER, where participants explored air pollution testing equipment, methods, and technologies for vehicles, with a focus on supporting national environmental policies related to zero-emission vehicles.
Transportation Pollution Research Center at NIER
- Learning from Korea Environmental Corporation (KECO)
Participants were introduced to Air Korea (Real-time Ambient Air Quality Disclosure System) and NAMIS (National Ambient Air Quality Monitoring Information System) at the Korea Environmental Corporation (KECO). These systems collect, select, and statistically process data measured from the national air pollution measurement network, providing essential data for air quality assessment.
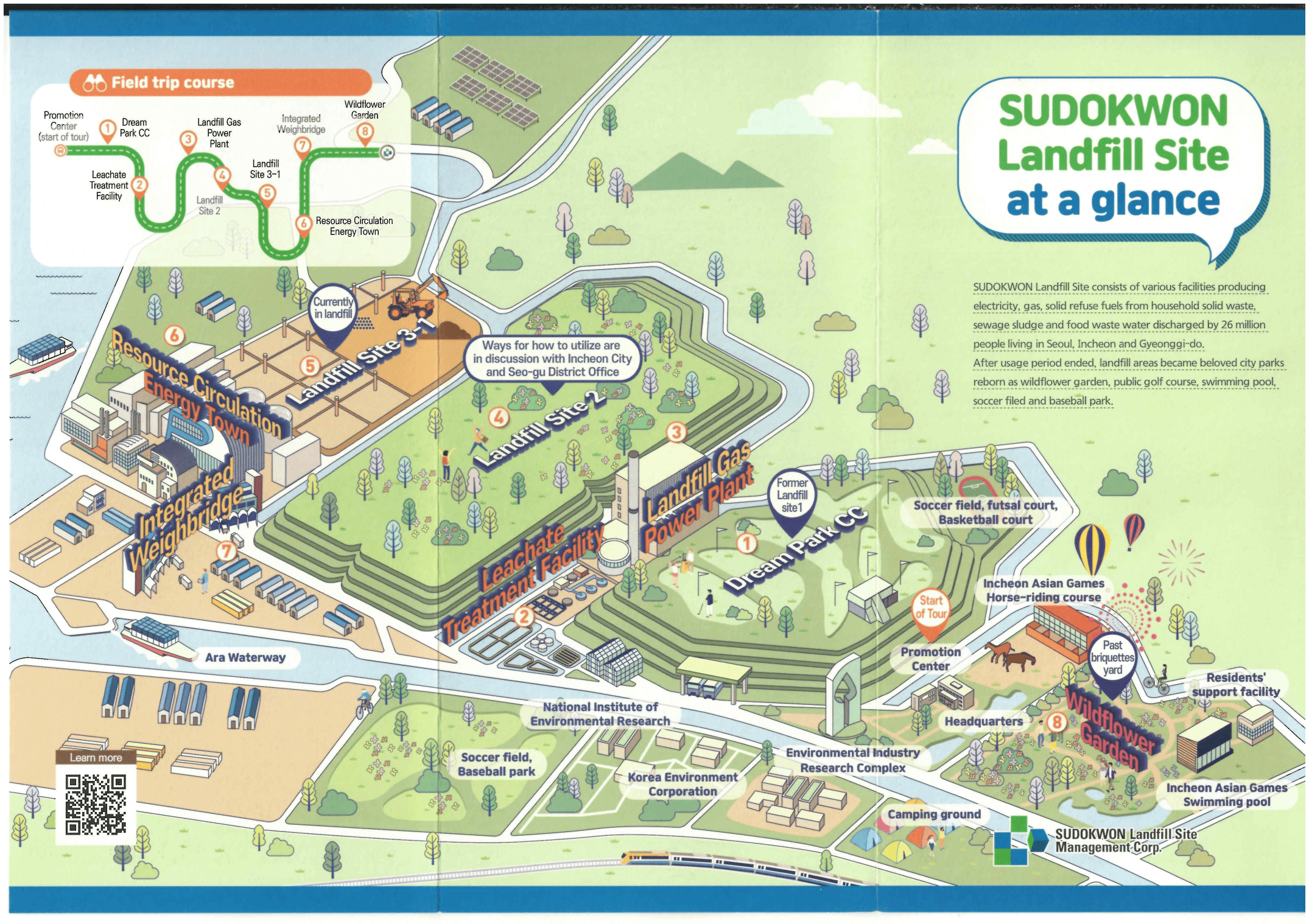
- Learning from Sudokwon Landfill Site
The study tour concluded with a visit to the Sudokwon Landfill site, offering a comprehensive view of sustainable waste management practices, including waste-to-energy conversion, innovative landfill designs and conversion of landfills into recreational facilities for community use. Furthermore, the presence of a leachate treatment facility and a 50 MW waste gas power plant underscored the commitment to environmental stewardship and resource optimization at the site.
Participants at the Sudokwon Landfill site
- Learning from Sharing Knowledge and Experience
The knowledge and experience gained during this study tour will be invaluable in strengthening air pollution control efforts in Bangladesh, India, and Thailand. The insights gained will be disseminated to stakeholders in the region, including policymakers, pollution control authorities, city municipal authorities, and the private sector.
Feedback from Participants on the Study Tour
At the conclusion of the Study Tour, participants shared their valuable feedback during a wrap-up session. Here's a summary of their insights:
Feedback on the Programs Visited:
- Participants were inspired by Korea's approach to air pollution control and urban planning, highlighting cutting-edge technology and innovative policies.
- They noticed a distinct gap in air pollution control between Korea and their respective countries, attributing it to technological advancements, well-defined policies, incentives, and regulatory measures.
- The visits to Seoul and Incheon Metropolitan Governments left a lasting impact, showcasing the effectiveness of regulatory measures, robust air pollution monitoring with IoT and real-time sensors, and satellite-based systems like GEMS and Pandora.
- Korea's impressive progress in promoting Electric Vehicles (EVs) stood out, offering potential for technology transfer and collaboration.
Key Takeaways for Participants:
- Participants recognized the urgent need for stronger air quality monitoring in their home countries, aiming to bridge the gap with Korea.
- Korea's substantial investment in technology demonstrated a strong commitment to addressing air pollution.
- Insights were gained into the importance of green infrastructure design and community involvement in pollution control efforts.
- The visit emphasized the necessity for increased collaboration between Korea and visiting countries, particularly in technology and regulatory measures.
Learning about the Relevance of Korea's Efforts:
- Korea's advanced technology holds promise as a valuable solution for visiting countries in combatting air pollution.
- Korea's focus on carbon capture in power generation, effective waste segregation, and Waste to Energy initiatives served as inspiration.
- Community participation increased through public disclosure of pollution data and innovative strategies like landfill conversion into recreational areas.
- Korea's success was attributed to political will, clear messaging (e.g., "Blue Sky Seoul"), and effective incentives and regulatory policies for cleaner vehicles.
Future Plans of Visiting Country Participants:
- Participants pledged to implement the insights gained from the tour in their respective countries.
- Visiting countries were encouraged to enhance their urban regulatory environments, standards, and green infrastructure within cities to catch up with Korea.
- Knowledge sharing, including city action plans, was deemed essential, with a strong emphasis on APCTT's role in disseminating Korean efforts and technology.
- Participants requested the continuation of the KECF project to facilitate the implementation of the acquired knowledge.
- Effective incentives and the promotion of Electric Vehicles were acknowledged as crucial elements in pollution control.
Results of Feedback Survey

